FIBRE:
A Fibre is a material which is several hundred times as long as its thick.That are very small in diameter in relation to their length.
TEXTILE FIBRE:
THE raw materials which is used to produce yarn in order to make fabric is called textile fibre.in other words . filament or fine strand of sufficient length,flexibility, and strength to be spun into yarns and woven into cloth is called textile fibre.
classification of textile :
1.classification according to their nature>>>>>>>>a)NATURAL FIBRE b) MANE MADE FIBRE
2
.CLASSIFICATION OF botanical>>>a)vegetable fiber eg:cotton,jute
classification zoological>>>>>>b)animal fibre eg:wool,silk
classification of chemical>>>>c)mane made fibre eg:polyester,polyethylene etc
3)classification according to their thermo plasticity >>>>>a)thermo plastic eg:polyester
b)Non-thermo plastic eg:cotton
4) classification according to length >>> a)staple b)filament
TEXTILE FIBRE PROPERTIES:
A)PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
B)MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
C)CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
A) PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
1.TENACITY
2.FIBRE MATURITY
3.ELONGATION
4.BURNING BEHAVE
5.PILLING &SWELLING
6.DURABILITY &EXTENSION
B)MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
1.STRENGTH
2.RIGIDITY
3.ELASTICITY
C) SOLUBILITY IN aqueous & organic salt.
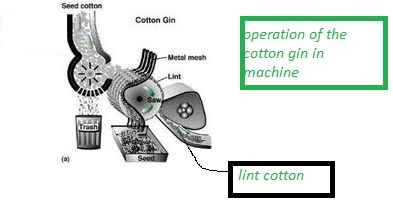
here difference type of fibre image that you can find visually
*cotton
jute
bamboo
banana